Experts concern over over virus
The reoccurance of virus Enterovirus 71 (EV71), a common cause of life-threatening illnesses for hand-foot-mouth (HFMD) patients, has made the disease dangerous and could easily spread into an outbreak, health experts have said.
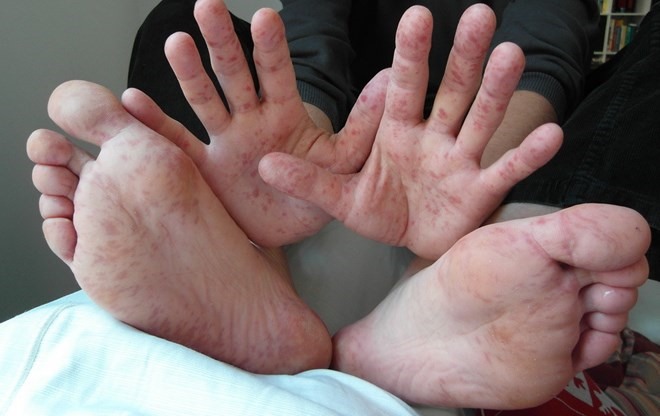 |
| The reoccurance of virus Enterovirus 71 (EV71), a common cause of life-threatening illnesses for hand-foot-mouth (HFMD) patients, has made the disease dangerous and could easily spread into an outbreak. – VNA/VNS |
Speaking at the online seminar on the abnormal development of the HFMD hosted by online newspaper Vietnamplus on Wednesday, health experts said all six deaths had tested positive for EV71.
HFMD caused by virus EV71 is likely to cause illnesses ranging from mild to serious with severe neurological and pulmonary complications, respiratory and heart failure that can lead to death. EV71 was the virus that caused HFMD outbreak in 2011 with 70,000 cases of infection and 150 deaths, they said.
Phan Trong Lan, director of HCM City’s Pasteur Institute said the HFMD was at its peak with more than 53,000 infected patients in the first nine months of this year.
Although the number of infection decreased compared to the same period of last year, the amount of deaths rose.
In HCM City’s Children No1 Hospital, the number of patients hospitalised for the disease has increased five times in the past three weeks leaving the hospital overcrowded.
Ha Noi-based Viet Nam-Cuba Hospital has received eight to ten HFDM patients each day recently.
The number of patients with serious illness stayed high in HCM City, posing the risk of outbreaks if preventive measures were not taken.
Lan said most of the six dead children were due to the disease were treated at home rather than going to the hospitals when showing symptoms of infection.
He said HFMD was commonly caused by the Coxsackie virus (A16) and Enterovirus (EV17). A16 was mild while EV71 could cause neurological complications, which was five times higher than other types of virus caused by the disease.
In the outbreak in 2011, 85% of deaths were positive with the virus.
There was currently no vaccine to protect against HFMD and going to hospital for treatment was the best solution to avoid complications if patients showed signs of infection.
In reply to questions on preventive measures, Dr Pham Hung, representative of the Ministry of Health’s Department of Preventive Medicine said the ministry has issued guidelines on HFMD treatment to all hospitals and health clinics nationwide.
It has also asked localities to implement treatment protocols and ensure sufficient facilities and medicines to minimise cases of complications and mortality.
Nguyen Thi Anh Xuan, head of Viet Nam-Cuba Hospital’s Peadiatrics Department said HFMD mainly affected children, especially those under three years old as it was a viral infection transmitted via digestion.
They also recommended preventive measures be carried out at schools to avoid infection among children.
(Source: VNS)